Everything You Need to Know About Machine Translation
Previously, we published a post about the reliability of Google Translate. The post got a surprising amount of interest from our users, so we thought we’d take some time to talk about the category that Google Translate falls into — machine translation.
How Does Machine Translation Work
Machine translation (MT) is automated, meaning it’s the translation of text by a computer with no human involvement. It works by using computer software to translate text from one language (source language) to another language (target language).
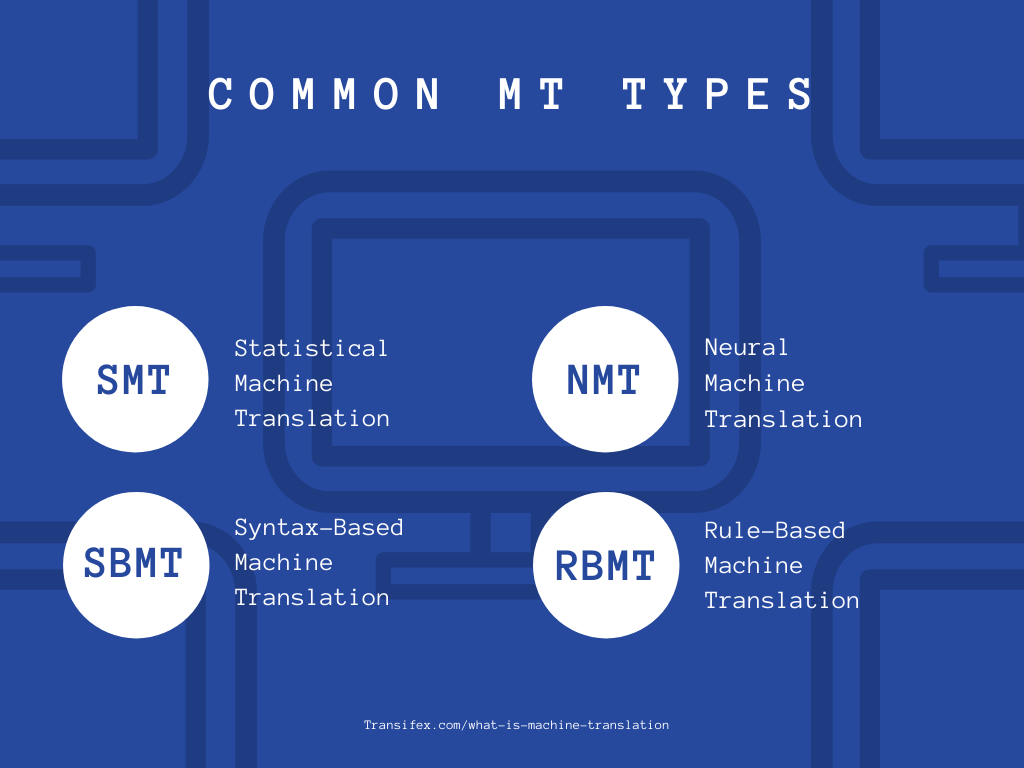
MT Types
There are plenty of MT types out there, but four of the most common ones are:
- Rule-based MT is, like its name suggests, based on a set of rules developed by language experts and programmers. These individuals reference dictionaries, general grammar rules, and semantic patterns of both languages to create a library of translation rules (software) that when run, deliver the appropriate translations of the source content in the desired target language. This library of manually built translation lexicons can also be adjusted over time to further improve translation quality.
- Statistical MT has no knowledge of language or grammatical rules. Statistical machine translation systems use computer algorithms that reference and analyze previously translated text and explore the millions of possibilities of how to order words and put smaller pieces of text together. The result is a database of translations that are based on the statistical likelihood that a certain word or phrase in the source language will be another word or phrase in the target language.
- Neural MT uses neural networks and artificial intelligence, often in combination with statistical MT methods, to get the job done. It’s one of the most highly complicated MTs, yet also one of the most effective.
- Syntax-Based MT translates syntactic units, instead of words. So, in some ways, it’s basically a sub-category of SMT (Statistical Machine Translation)
There are also Hybrid Machine Translation tools that use two or more MT approaches on a single piece of software. More about all that on our updated blogpost.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Rules-based and statistical machine translation can be compared to one another, but MT is generally looked at as a single solution as opposed to two different options. The general advantages and disadvantages of using machine translation to translate content, especially for businesses, include:
Advantages
- Increased productivity and ability deliver translations faster
- Faster translations means reduced time-to-market
- Flexibility from a number of machine translation engines
Disadvantages
- MT can’t account for certain phrases because of lack of context
- It’s difficult for machine translation to accurately translate nuances and slang
- Complicated or industry specific terms (i.e. medical terminology) may not be easily translated
- Specific errors are hard to predict and difficult to correct
- Content in the target language can feel choppy or pieced together
Machine Translation vs. Human Translation
For businesses interested in translating their digital content into other languages, machine translation presents itself as an easy fix to a complicated problem. Machine translation is mainly seen as:
- A fast solution. Depending on how much content needs to be translated, machine translation can provide translated content in a matter of seconds, whereas human translators will take more time. Time spent finding, vetting, and managing a team of translators must also be taken into account.
- An affordable solution. There are many translation software providers that can provide machine translations for little to no cost, making it an affordable solution for businesses who may not be able to afford professional translations.
Can MT Replace Human Translation?
Now all this builds up to the question of the hour — can machine translation replace human translation? Yes, it can replace human translation, and there are a few instances when MT is a better option. For instance, service-related companies often use machine translation to help customers via instant chat or respond quickly to emails.
But, (and there’s always a but) if you’re translating more in-depth content, like your website or mobile app, using machine translation puts your brand at risk. In the best case, improper translations make your website or app look unprofessional. In the worst case, improper translations offend users in your target locale. The cost of poor translations goes beyond monetary loss and has the potential to impact how users perceive your brand. The negative backlash from an entire culture or audience will cost you far more than hiring a professional translator or native speaker to begin with.
Are you willing to put your brand in the hands of MT? While most brands aren’t, the answer should always be never! Protect your brand and learn how to get reliable, continuous, and quality translations with help from the Transifex localization platform. And if you’d like to see how the platform works, request a demo today.